When it comes to carbon monoxide safety, we all have a role to play to help keep you and your family safe.
What is Carbon Monoxide?
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colourless, odourless, tasteless and toxic gas and is often referred to as the "Silent Killer." When inhaled it inhibits the blood's capacity to transport oxygen throughout the body. It can poison the body quickly in high concentrations, or slowly over long periods of time.
What are the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning?

Exposure to CO can cause flu-like symptoms such as
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Burning eyes
- Confusion
- Drowsiness
- Loss of consciousness
In severe cases, CO poisoning can cause brain damage and death.
The elderly, children and people with heart or respiratory conditions may be particularly sensitive to CO.
How is carbon monoxide generated in the home?
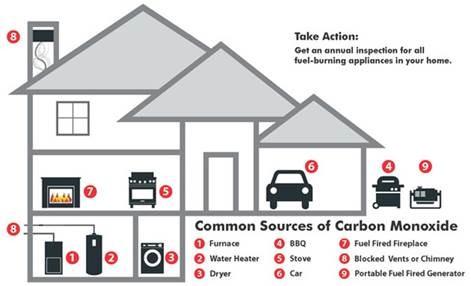
Carbon monoxide is a by-product of incomplete combustion of fuels such as natural gas, propane, heating oil, kerosene, coal, charcoal, gasoline or wood.
This incomplete combustion can occur in any device that depends on burning for energy or heat, such as
- Furnace
- Gas water heater
- Gas fireplace
- Gas stove
- Gas dryer
- Gas barbecue
- Portable generators
- Fuel-burning space heaters
- Any gas-powered vehicle or engine
- Automobiles left running in attached garages
- Gas barbecues operated inside the house
- Grills or kerosene heaters that are not properly vented
- Chimneys or vents that are dirty or plugged
When properly installed, maintained and vented, any CO produced by these devices will not stay inside the home.
Most Ontario households have, on average, four to six appliances that produce carbon monoxide.
The best way to ensure that you and your family are not exposed to carbon monoxide is to eliminate this poisonous gas at the source. Have a trained, certified technician check your furnace, gas, stove, fireplace or fuel-burning appliances on a yearly basis.
Where should a CO alarm be located in the home?
- Outside all sleeping areas of your home or cottage
- In your RV and boat cabin
- In your boathouse
Proper placement of a CO alarm is important. In general, the human body is most vulnerable to the effects of CO during sleeping hours, so an alarm should be located in or as near as possible to the sleeping area of the home.
If only one alarm is being installed, it should be located outside the sleeping area, where it can wake you if you are asleep.
Where sleeping areas are located in separate parts of the home, an alarm should be provided outside of each area.
Additional CO alarms should be placed on each level of a residence and in other rooms where combustion devices are located (such as in a room that contains a solid fuel-fired appliance, gas clothes dryer or natural gas furnace), or adjacent to potential sources of CO (such as in a teenager's room or granny suite located adjacent to an attached garage).
Unlike smoke, which rises to the ceiling, CO mixes with the air. Recognizing this, a CO alarm should be located at knee height (which is about the same as prone sleeping height). Due to the possibility of tampering or damage by pets, children, vacuum cleaners and the like, it may be located up to chest height. To work properly, a CO alarm should not be blocked by furniture, draperies or other obstructions to normal airflow.
If a combination smoke/carbon monoxide alarm is used, it should be located on the ceiling, to ensure that it will detect smoke effectively.
Always refer to the manufacturer's instructions for additional information regarding proper installation, use and maintenance.
Alarm testing
- Remember to test your CO alarm and smoke alarm once a month by pushing the test button on the unit.
- Replace batteries once a year, including back-up batteries for plug-in alarms.
- A good habit is to change the batteries every fall or spring when you change your clocks.
Remember
Like most things, CO alarms wear out over time. Check the manufacturer’s instructions to find out when your particular unit should be replaced (usually after 7-10 years for CO alarms and 10 years for smoke alarms).
Visit the TSSA's ‘Silent Killer’ page for more information on CO and how you can protect yourself.